题目:Hydration-Mediated Morphological and Electronic Tuning in Layered Double Perovskites for p-Type Transparent Conductors
作者:Jun Liu,[1] Jianen Zhang,[1][2] Qi Xue,*[3] Huiying Gao, [3] Shirui Zhang, [3] Jinfeng Xie,[1] Li Guan,[2] Xiaohong Zhang,*[4] He Huang*[1]
单位:
[1]Jun Liu, Jianen Zhang, Jinfeng Xie, Prof. Dr. He Huang, School of Optoelectronic Science and Engineering, Soochow University, 215006, Suzhou, P. R. China.
[2]Jianen Zhang, Prof. Dr. Li Guan, Key Laboratory of High-precision Computation and Application of Quantum Field Theory of Hebei Province, College of Physics Science and Technology, Hebei University, 071002, Baoding, P. R. China.
[3]Dr. Qi Xue, Huiying Gao, Shirui Zhang, School of Physical Science and Technology, Soochow University, 215006, Suzhou, P. R. China.
[4]Prof. Dr. Xiaohong Zhang, Institute of Functional Nano and Soft Materials (FUNSOM), Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Carbon-Based Functional Materials and Devices, Soochow University, 215123, Suzhou, P. R. China.
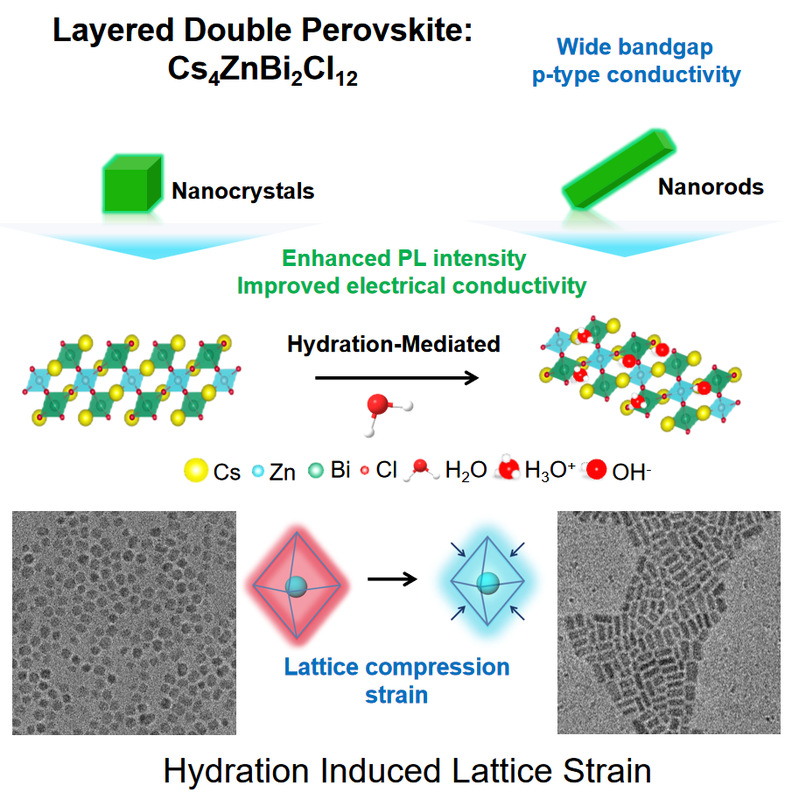
摘要:The development of high-performance transparent conductors (TCs) is critical for advancing transparent electronics and optoelectronic devices. While n-type TCs are well established, the development of p-type TCs remains hindered by the limited availability of suitable materials. In this study, the layered double perovskite Cs4ZnBi2Cl12 was synthesized as a promising p-type transparent conductor, which exhibits a wide direct bandgap of 3.56 eV and intrinsic p-type conductivity. A hydration-mediated strategy was developed to trigger a near-spherical nanocrystal-to-nanorod transformation and modulate the electronic structure. First-principles calculations clarify that the lattice compressive strain induced by hydration significantly reduce the hole effective mass while increasing conductivity from 8.99 to 9.21 mS cm-1, outperforming traditional p-type TCs, such as CuAlO2 (3.4 mS cm-1) and SrCu2O2 (0.48 mS cm-1). These findings not only provide experimental validation of theoretical predictions regarding Cs4ZnBi2Cl12 as a p-type TC but also establish a hydration strategy for optimizing the optical and electrical performance of layered double perovskites.
高性能透明导体(TCs)的发展对推动透明电子学与光电器件具有关键意义。尽管 n 型 TCs 已经相对成熟,但 p 型 TCs 的发展仍受限于合适材料的缺乏。本研究中,成功合成了层状双钙钛矿 Cs4ZnBi2Cl12,证明其是一种极具潜力的 p 型透明导体,该材料具有 3.56 eV 的宽直接带隙以及内禀的 p 型导电性。本文提出了一种水合调控策略,可诱导Cs4ZnBi2Cl12 纳米晶由近球形向纳米棒转变,并实现其电子结构的调控。第一性原理计算进一步揭示,水合引发的晶格压缩应变显著降低了空穴有效质量,使电导率由 8.99 mS·cm-1 提升至 9.21 mS·cm-1,优于传统 p 型 TCs(如 CuAlO2:3.4 mS cm-1,SrCu2O2:0.48 mS cm-1)。该研究不仅为Cs4ZnBi2Cl12 作为 p 型 TC 的理论预测提供了实验验证,也建立了一种利用水合实现层状双钙钛矿光学与电学性能优化的新策略。
影响因子:17.5
链接:https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2590238525005211?dgcid=author
